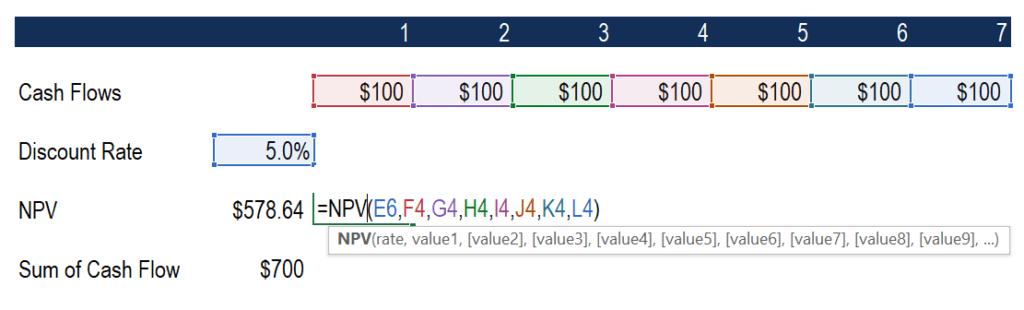
Content
Note, this would usually be quoted by a lender as a nominal rate of 12% per year, compounded monthly. Only those interest rates placed on a comparable basis may be compared. Nominal interest rates can be compared if the nominal rates have the same time period and same compounding period. Otherwise, translating the nominal rates into effective rates will allow them to be compared to each other. For example, a rate quoted as 10% is assumed to mean a nominal interest rate of 10% per year, compounded yearly. Since the time and compounding periods are the same, the nominal and effective rate will also be the same.
What is a nominal rate of interest?
The nominal interest rate (or money interest rate) is the percentage increase in money you pay the lender for the use of the money you borrowed.
Now imagine there is a faucet above the bucket dripping purchasing power into the bucket. But the bucket also has a small hole in the bottom, allowing your purchasing power to leak out. If the bucket has purchasing power dripping in and leaking out at the same time, what will happen to the level of your purchasing nominal interest rate example power in the bucket? For example, gasoline prices have a lot of upward and downward movement, sometimes even from day to day. But rapidly rising or falling gasoline prices, or for that matter rising or falling prices of any single item, don’t necessarily mean that the rate of inflation is increasing or decreasing.
How does nominal interest rate differ from real interest rates?
In this analysis, the nominal rate is the stated rate, and the real interest rate is the interest after the expected losses due to inflation. Since the future inflation rate can only be estimated, the ex ante and ex post real interest rates may be different; the premium paid to actual inflation . Lenders start from the real return they want to receive and set their own nominal interest rates. They add together their expected real rate of return with their expectation of the inflation rate, and this is how they arrive at the nominal interest rate they charge on the money they lend.
Unexpected inflation creates winners and losers, and borrowers definitely benefit when unexpected inflation results in them paying lower real interest rates. Lenders, on the other hand, are the losers in this case and are not satisfied with the lower real rate. This assumes that the interest rate is fixed; otherwise banks would increase the interest rate along with the inflation rate.
Nominal and Real Interest Rate Examples
For simplicity, we will discuss interest rates in terms of what someone would pay, or receive, for a loan. Many portfolio simulations and pricing models for derivatives use a continuously compounded interest rate formula. Dividing 115 by the interest rate yields the number of years required to triple an investment. So a 10% rate of return will take about 11.5 years to triple the principal.
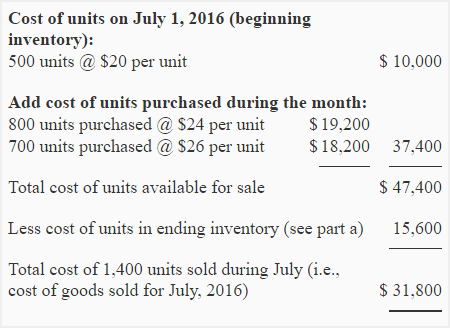
The nominal and effective interest rates are not always different. If the compounding period is exactly one year, the nominal rate and effective rate will be the same. Consider a bond with an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded annually.
How Do You Calculate the Effective Rate If Nominal Rate Is Known?
For example, suppose we want to know what the nominal annual rate, compounded monthly, would have to be to provide an effective annual rate of 10%. Recall that with nominal interest rates we need to provide 1) a stated rate per period, and 2) the number of times interest is compounded during that period. So, in this case we would say that we have a nominal rate of 6% per year, compounded quarterly. Do you know the difference between nominal and real interest rates?
- However, suppose the time and compounding periods were not the same.
- Note also the adjustment made to the local borrowing cost for country risk.
- Different effective interest rates can be compared directly since they’ve been adjusted to reflect the effect of compounding.
In the final part of our exercise, we’ll assume the actual inflation rate was substantially higher than the anticipated rate of the lender. The real interest rate represents the opportunity cost of lending money out. The nominal interest rate is one you’ll commonly see quoted at your local bank or credit union. For example, Car loans are available at 10% of the interest rate. Nominal Interest Rate FormulaNominal Interest rate refers to the interest rate without the adjustment of inflation.
14 The Fisher Equation: Nominal and Real Interest Rates
Without accounting for inflation, the actual costs or returns can vary widely as the purchasing power of money changes over time. Effective interest rate is considered a more accurate measure of interest. It is calculated based on the nominal interest rate and its compounding periods. Different effective interest rates can be compared directly since they’ve been adjusted to reflect the effect of compounding.
- And we have to consider continuous compounding interest rate of 12%.
- One lender offers a 25-year mortgage with interest at 5% compounded semi-annually, and another offers a 20-year mortgage with interest at 4.8% compounded monthly.
- Consumers who weren’t inflation savvy may have believed that a 9 percent nominal interest rate on their deposits would make them rich.
- The reason why the money market uses the nominal interest rate is that, by definition, the nominal interest rate ____ the rate of inflation.
- Interest is the money that a lender receives from a borrower in exchange for the borrower’s use of the lender’s money .
- On a 1-year US bond is 5% and the nominal interest rate in Mexico for a bond of the same maturity is 10%.
- Information is from sources deemed reliable on the date of publication, but Robinhood does not guarantee its accuracy.
Most firms in emerging markets are not rated; to determine which home-country interest rate to select, it is necessary to assign a credit rating to the local firm. This “synthetic” credit rating is obtained by comparing financial ratios for the target firm with those used by US rating agencies. The estimate of the unrated firm’s credit rating may be obtained by comparing interest coverage ratios used by S&P with the firm’s interest coverage ratio to determine how S&P would rate the firm. In practice, the sovereign bond spread is computed from a bond with the same maturity as the US benchmark 10-year Treasury bond used to compute the risk-free rate for calculating the cost of equity. Notice this is the same result we manually calculated in the effective interest rate discussion above. In other words, if we were to use our bank account example again, then at the end of the first quarter we are owed $100 x 1.015 in interest.
Related: nicole elizabeth solomon, chattanooga police department open records, juniper property partners oxford, ohio, advantages of microscope, , evergreen cemetery tuscaloosa, claus von bulow net worth 2018, , jefferson parish noise ordinance hours, pleasants county wv arrests, saratogian police blotter, lennar homes orlando office, henry james zahn, cuanto es 7 elevado a la 70 potencia, child protective services detroit,